Naturally occurring bacteria that is found in water and soil, Legionella is harmless when it is present in small concentrations. However, when they are allowed to colonise freely and thrive in their surroundings, Legionella can become an extreme health risk. The ideal temperatures for the bacteria to colonise are in the range of 35 degrees Celsius to 46 degrees Celsius. This is further accelerated if there is any presence of organic matter, such as algae, for it to feed on. Should the Legionella bacteria ever colonise in the respiratory tract of a human being, it can cause Legionnaires’ disease. Legionnaires’ disease, also called Legionellosis is an acute form of pneumonia, which can, in many cases, result in death. Typically, the disease is contracted due to breathing in water aerosols that are contaminated with the bacteria. It can also be contracted when water containing the bacteria is breathed into the lungs because of choking while swallowing, ingesting or drinking.
Naturally occurring bacteria that is found in water and soil, Legionella is harmless when it is present in small concentrations. However, when they are allowed to colonise freely and thrive in their surroundings, Legionella can become an extreme health risk. The ideal temperatures for the bacteria to colonise are in the range of 35 degrees Celsius to 46 degrees Celsius. This is further accelerated if there is any presence of organic matter, such as algae, for it to feed on. Should the Legionella bacteria ever colonise in the respiratory tract of a human being, it can cause Legionnaires’ disease. Legionnaires’ disease, also called Legionellosis is an acute form of pneumonia, which can, in many cases, result in death. Typically, the disease is contracted due to breathing in water aerosols that are contaminated with the bacteria. It can also be contracted when water containing the bacteria is breathed into the lungs because of choking while swallowing, ingesting or drinking.
When a person gets infected, they show the usual symptoms of the flu. These include minor symptoms such as muscle aches and headaches. Within no time, they will move on to more serious symptoms such as chills, diarrhoea, high fever, nausea and vomiting. They will also experience difficulty in breathing, dry coughs and a pain in the chest. Studies show that the drug has a mortality rate of about 30%. Those who are over the age of 50 and have chronic respiratory issues, lung disease, or are heavy smokers and drinker, are at risk, in particular. Moreover, people who have diabetes or weak immune systems, in general, are also at risk.
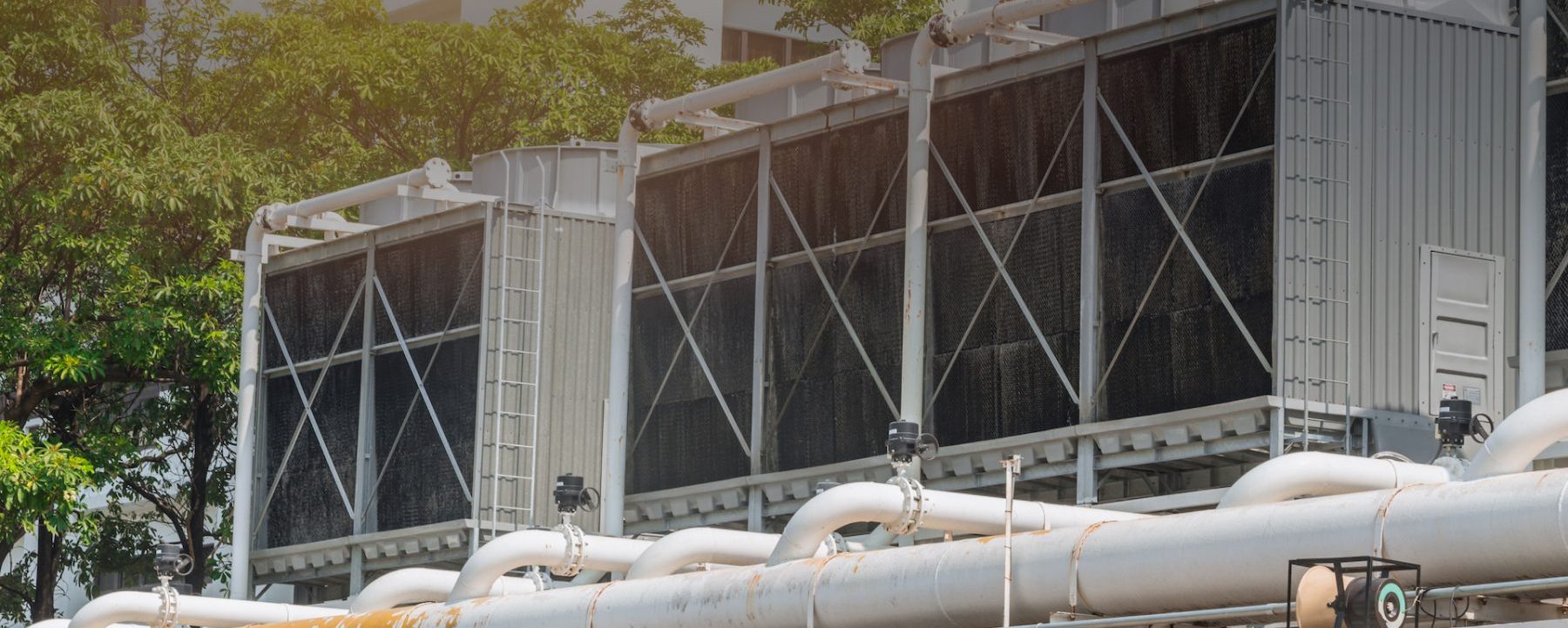
Cooling Towers and the Legionnaires’ Disease: What’s the connection?
Research has shown that cooling towers, due to the warm water, form perfect breeding grounds for this bacterium to thrive and colonise. They are often investigated and found to be the main source of outbreaks of the Legionnaires’ disease. These outbreaks are always expected, especially during the warmer months. This is because it creates the ideal conditions in the warm water systems. Improved methods of detection have made it easier to spot the increase in the outbreaks; however, it does nothing to stop the infections. It is extremely important to maintain the water systems of a facility and keep them healthy in order to lower the risk of an outbreak. There are several new measures that need to be followed as well, but it is confusing to understand the new laws for an owner, an engineer or a facility manager. One can get complete assistance by approaching cooling tower legionella services for help.
Controlling the Outbreak of Legionnaires’ Disease
HydroChem is the leader in commercial and industrial water treatment in Australia since 1977. They are experts at the requirements of both the national and state governments and are aware of how the new laws affect managers and owners. The company has set up a website on Legionella Guidelines that one should follow to make sure that they are complying with the laws. It is known to provide the best cooling tower legionella services across Australia due to their experience and expert knowledge.